single chromosome plus plasmids (PROKARYOTES or EUKARYOTES)
Click to see answer
PROKARYOTES
Click to see question
single chromosome plus plasmids (PROKARYOTES or EUKARYOTES)
PROKARYOTES
circular chromosome (PROKARYOTES or EUKARYOTES)
PROKARYOTES
made of chromatin, a nucleoprotein (DNA coiled around histone proteins)
EUKARYOTES
many chromosomes (PROKARYOTES or EUKARYOTES)
EUKARYOTES
made only of DNA (PROKARYOTES or EUKARYOTES)
PROKARYOTES
linear chromosomes (PROKARYOTES or EUKARYOTES)
EUKARYOTES
found in cytoplasm (PROKARYOTES or EUKARYOTES)
PROKARYOTES
found in a nucleus
EUKARYOTES
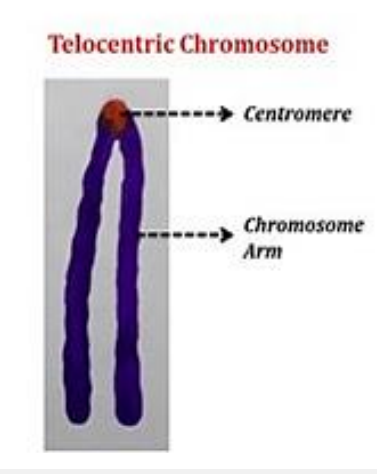
Telocentric Chromosome
At the beginning of mitosis, they can be seen to consist of two threads (sister chromatids) joined by a __________ (CHROMOSOMES IN EUKARYOTES)
centromere
copies chromosomes, then the cell grows, then goes through mitosis to organize chromosomes in two equal groups
EUKARYOTES
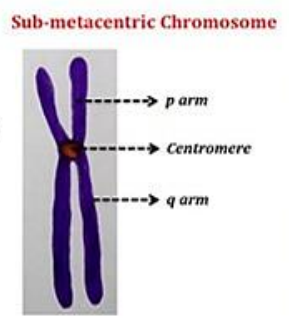
Sub-metacentric Chromosome
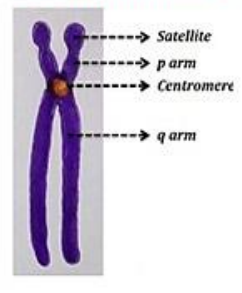
Acrocentric Chromosome
Multicellular organisms copy their chromosomes before cell division. ; They must grow to a mature size.
Interphase
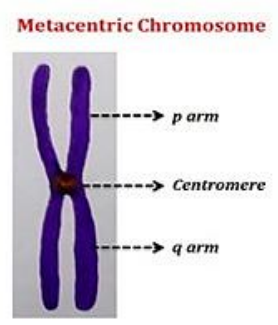
Metacentric Chromosome
Chromosomes are analysed by organising them into a ____________________
KARYOTYPE
The X and the Y chromosomes are called
Sex Chromosomes
The nucleus divides, distributing the chromosomes into two equal groups
mitosis
The cytoplasm then divides each part taking a nucleus
cytokinesis
a special type of cell division ; used to make sex cells
Meiosis
halves the numbers of chromosomes ; picks one chromosome from each pair at random and places them in a sex cell. This results in enormous variation amongst the sex cells.
Meiosis
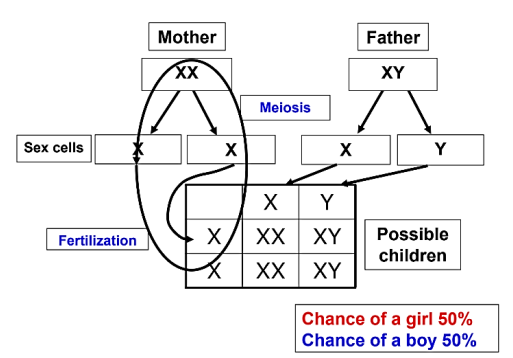
Inheritance of Gender
Blood type is also __________
phenotype