possess many organelles
Click to see answer
eukaryotic cells
Click to see question
possess many organelles
eukaryotic cells
Cell wall present in _________________
bacteria, fungi, algae, and plant cell
parts of phospholipids
Hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic tail
Present in almost all types of cells
plasma membrane / cell membrane
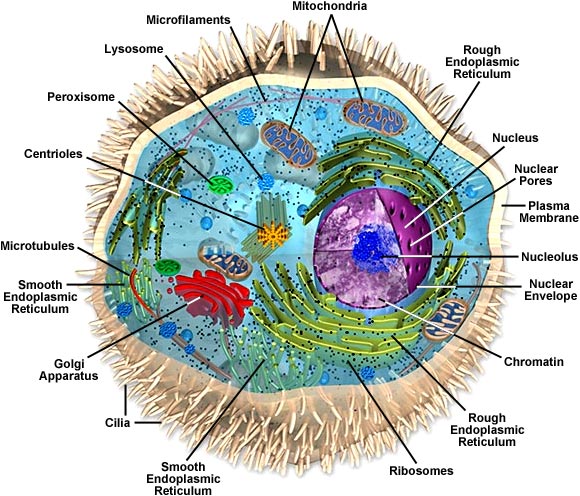
Powerhouse of the cell
Mitochondria
Complete the breakdown of glucose, producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Mitochondria
unicellular organisms
prokaryotic cells
multicellular organisms
eukaryotic cells
organelles not bound by membranes
prokaryotic cells
ribosomes are present in what type of endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
first cell type on earth
prokaryotic cells
Cell Membrane (Image Only) - baka need mo mahalll e hihi
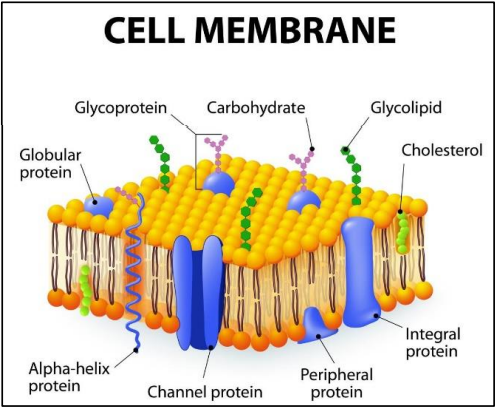
movement of molecules from high to low concentration
active transport
main function of golgi complex
links carbohydrates and complex protein
made of RNA & protein
ribosomes
Contains cell contents
plasma membrane / cell membrane
phospholipid contains how many regions
2
movement of molecules from low to high concentration
passive transport
nucleus bound by membrane
eukaryotic cells
Cell wall absent in
animal cell and protozoa
what are the 5 biochemical composition of plasma membrane
Phospholipids
Glycolipid
Cholesterol
Protein
Carbohydrates
describes fluid nature of a lipid bilayer with proteins
Fluid mosaic model
synthesizes proteins by the station messenger (mRNA) into peptide sequences followed by packaging of proteins/ endoplasmic reticulum
ribosomes
3 principles of cell theory
1) Smallest living unit of structure & function of all organisms.
2) All things are made up of cells.
3) All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
made up of a lipid by layer/ double layer of lipids known as _______________
phospholipid by layer
Fluid portion of the cytoplasm
cytosol
region of DNA concentration
Nucleoid
Double layer of phospholipids & proteins
plasma membrane / cell membrane
Anatomy of Animal Cell (Image Only)
most abundant component of plasma membrane
Phospholipids
in order to transport certain substances from the cell outside (vice versa), __________ is needed during the process
ATP
All organelles reside the __________
cytoplasm
Molecules that move freely across the plasma membrane
Water, carbon dioxide, Ammonia, Oxygen
the protein packaging and transport center of the cell
golgi complex
cell type of bacteria and archaea
prokaryotic cells
includes fungi, protists, plant, and animal cells, protozoan
eukaryotic cells
transports materials throughout the cell
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
digests lipids (Strictosidine synthase – STR enzyme, metabolizes blood, breakdowns drugs steroids and carbohydrates, and partake in muscle contraction)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
breaks down materials for digestion
lysosome
well-developed in cells, active in protein synthesis (e.g. plasma cells, russall bodies of plasma cells)
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
site of the synthesis of lysosomal enzymes and proteins for extracellular use
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
purpose of hydrolytic enzymes
once lysosome releases hydrolytic enzymes, it will digest the cell/ tissues
produces hydrolytic enzymes
lysosome
control center of the cell
nucleus
contains the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) code for the cell coiled into chromosomes
nucleus
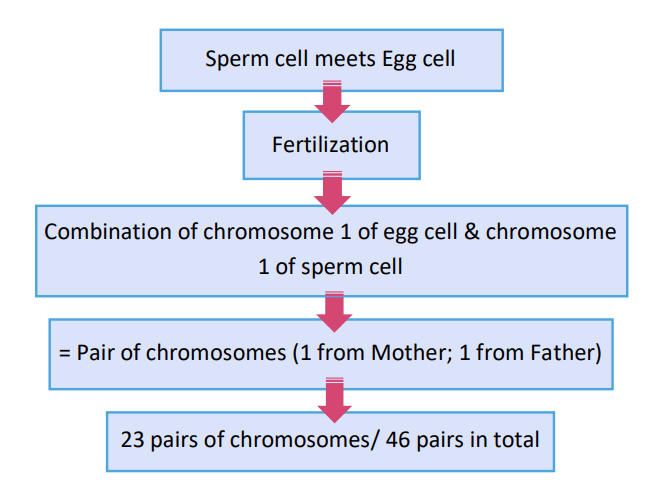
human has __________ pairs of chromosomes
23
the 23rd pair of chromosome is ____________
sex chromosome
1 to 22 pair of chromosome is
autosomes
protects and maintains the shape of the cell
cell wall
rigid and strong wall (plant cell)
cell wall
uses light energy to make ATP & sugar
chloroplast
where photosynthesis takes place
chloroplast
contains chlorophyll. makes plants green
chloroplast
maintains purgor pressure (force within the cell that pushes plasma membrane against the cell wall)
central vacuole
series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication)
Cell Cycle
Cell grows ; Cell accumulates nutrients needed for mitosis > replicating its DNA before it moves on to mitosis proper
Interphase
from the end of the previous M phase until the beginning of DNA synthesis ; Growth phase ; RNA organelles and proteins are synthesized (Interphase)
G1 (Gap) Phase
DNA is replicated, and chromosomes form sister chromatids ; The amount of DNA in the cell has effectively doubled, though the ploidy of the cell remains the same(Interphase)
S Phase
Mitochondria divide ; Precursors of spindle fibers are synthesized ; last ‘til the cell enters mitosis (Interphase)
G2 Phase
Not part of the interphase ; Non-replicating cells are found in a stage of the cell cycle called _________ ; Quiescent (dormant) – undergo G1 phase again ; Senescent (aging/ deteriorating) – DNA defective Cells generally enter the __________ phase from G1
G0 Phase
a process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the chromosome in its cell nucleus into two identical sets in two nuclei.
Mitotic (M) phase / Mitosis
Mitosis begins (cell begins to divide) ; Centrioles (poles) appear and begin to move to opposite end of the cell ; Spindle fibers form between the poles ; Nuclear envelope disappears
Prophase
Chromatids (pairs of chromosomes) attach to the spindle fibers ; All chromosomes lined up ate the equator
Metaphase
Chromatids (pairs of chromosomes) separate and begin to move to opposite ends of cell
Anaphase
occurs after mitosis ; cell membrane moves inward to create two daughter cells – each with its own nucleus w/ identical chromosomes
Cytokinesis
Two new nuclei form ; Chromosomes appear as chromatin (threads rather than rods) ; Mitosis ends
Telophase
The special cell division that converts diploid body cells into the haploid gametes. ; Process that reduces the chromosome number in such a way that the daughter nuclei only receive one member of each homologous pair of chromosomes. Think of it as a double mitotic division with only a single S phase ; Takes 2 cell divisions: M1 and M2, with no DNA synthesis between
Meiosis
“crossing over”, also called “recombination” ; In crossing over, homologous chromosomes pair up, and exchange segments by breaking and rejoining at identical locations. (Meiosis 1)
Prophase I
Much like the cytokinesis of Mitosis, in which the cells will be separated totally under this process ; End of PMAT 1. (Meiosis 1)
Interkinesis
Cytoplasm divided into 2 cells, each of which has 1 haploid set of dyad chromosomes (Meiosis 1)
Telophase I
Dyad chromosomes line up singly on the cell equator (equatorial plate) (Meiosis II)
Metaphase II
Cytpolasm divided into 2 cells. ; Not totally separated, cleavage furrow still visible. ; Cell membrane attached from each cells. ; Will undergo Interkinesis II to totally separate each cells
Telophase II
Chromosomes condense and spindle fiber forms ; Centrioles move to the opposite ends of the cell. (Meiosis II)
Prophase II
Centromeres divide, chromosomes are now monads which get pulled to opposite poles. (Meiosis II)
Anaphase II
how many chromosomes does sperm cell and egg cell have?
23
Specialized cells (gametes) only undergo the __________ phase.
Meiosis
Additional Notes (Just flip)
Eukaryotic cells have more complicated process of replication/ duplication as it undergoes mitosis and meiosis.
Interphase is not part of mitosis, it is a preparation for mitosis.
prokaryotic cells like bacteria undergo on what kind of division
binary fission
process of having 23 pairs of chromosomes
Spindle fibers pull the two homologous chromosomes to opposite poles ; However, centromeres don’t divide and the chromosomes remain dyads. (Meiosis 1)
Anaphase I
Pairs of homologous chromosomes line up together (equatorial plate) ; Spindle fibers coming from the centrioles will then attach to the centromere of each chromosome ; However, there are two chromosomes which are both complete. (Meiosis 1)
Metaphase I